– Dr Pavana Kamath
Dentists do far more than just restore teeth, however we cannot deny the fact that restorative or operative dentistry is one of the most commonly practised form of dentistry, because dental caries has been the most common oral disease. An average dentist spends a significant amount of time in his practice restoring teeth and performing root canal therapy. (1)
Globally, it is estimated that 2.3 billion people suffer from caries of permanent teeth and more than 530 million children suffer from caries of primary teeth.

Operative dentistry is physically demanding in some very specific ways. A successful practice essentially requires a healthy back, neck, shoulder,wrist and hand, and above all a good vision to develop the required skills and experience.(2)
Sight is man's most highly developed sense. A dentist needs good vision for learning, using tools and devices. For the inexperienced and unskilled, vision is essential for acquiring the skills while for the skilled, vision is essential for maintaining optimal performance in one’s respective field of work. For the young, as well as the elderly eyesight is the principal sensory pathway of learning and communication. For all, vision is a vital tool for functioning in daily activities, for perceiving ,and for achieving personal fulfilment in respective field of work. Hence it is evident that good vision is an essential requirement for every dentist for his daily dental practice.(3)
A successful practice requires constant upgradation both in skills as well as armamentarium. Investment in advanced technology is an individual choice and plays an important role in the quality of dental practice. A few tools in dentistry are invaluable both in terms of upgradation in technology as well as in maintaining good health and vision. Magnification tools rank among the first in them.
Microdentistry can be defined as the practice of minimally invasive dentistry with the aid of any optical device that magnifies the operative field. As a direct consequence of the better visualization obtained, treatment can be more precise and less invasive, thus preserving the oral tissues and dental structures from unnecessary substance loss during procedures such as diagnosis, caries removal, and cavity preparation. This concept can and should be applied to dentistry as a whole, not only to those specialties where we “need to see more.” (4)
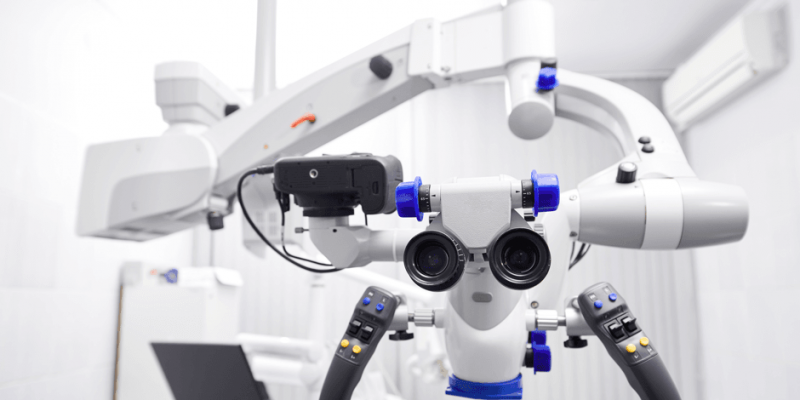
Dental loupes and the dental operating microscope are widely used as a source of magnification in dentistry. Technical developments in a dental operating microscope such as autofocus, magnetic fixation, charge-coupled device and high-definition digital cameras enhance the precision while also improving ergonomics .
MICROSCOPE & ENDODONTICS: The role of an operating microscope (OM) in endodontics, both non surgical as well as surgical, is incomparable. It is extremely useful in locating calcified or missed canals and removing obstacles from the pulp chamber or root canal system, as well as stones or separated instruments. A routine root canal procedure can be executed with precision, accuracy and superior documentation.
The biggest revolution due to the introduction of the microscope in nonsurgical endodontics is in the area of re-treatment. Every single procedure that was previously performed using tactile sensation alone, can today be performed with complete vision, precision and control.
Advances in microsurgical endodontics has ensured that the facility is an integral part of the endodontic treatment plan and not just a last option to salvage the diseased tooth. While identification of anatomical variations like lateral canals, isthmus, fins etc has become the norm, it ensures removal of inflammatory tissue as well as three -dimensional endodontic management of the apical third of the root canal,which is vital to the success of the rendered treatment.(5)
MICROSCOPE & SURGERY:
- The advantages of the dental OM in implantology are innumerable especially in clinical evaluation, diagnosis, sinus lift procedures, soft tissue management, and photographic and video documentation.
- Periodontal microsurgery helps in the refinement of basic surgical techniques made possible by the improved visual acuity gained with the use of the surgical microscope.
In the hands of a trained and experienced clinician, microsurgery offers enhanced outcomes which would be challenging with traditional macrosurgery, especially in terms of wound healing and minimal tissue trauma. The use of an OM in periodontal and prosthodontic treatment allows for smoother surface roughness of preparations and superior marginal fit of restorations to abutments.
LEARNING CURVE WITH MICROSCOPE: Several studies have emphasised that the occasional or intermittent use of the OM during endodontic treatment had a negative effect on the final result, as it increased the duration of appointments and disrupted the clinical procedures. Therefore, the operators were advised to perform the whole treatment session under microscope. Learning how to work efficiently with the dental operating microscope is as important as investing in a good one.
The tactile experience is often replaced by precise and crisp details visible of the area in question. The most easily recognized benefit for the clinician is the improvement in fine motor skills. Visual assessment of marginal fit using the microscope is significantly more accurate than tactile examination with an explorer.
INVESTING IN A GOOD MICROSCOPE: The time consumed in learning to use the dental OM effectively is worth the effort, the deep learning curve is attributed to mastering the hand eye coordination and the ergonomics associated with the working. This can be easily mastered by chosing the right microscope according to our work requirements.
Some important aspects to be considered while chosing a microscope include
- Optical requirements and quality.
- The ability of the objective lens to display movement multidirectionally and spatially with minimal effort and movement (easy manoeuvrability).
- Features the ability to move both vertically and horizontally to accommodate the work requirements of both the operator and the assistant,hence creating an optimal work environment.
- Equipped with features making it suitable for use in all specialities with minimal manoeuvring.
- Adapatability to design ergonomic compatibility with different dental chair designs.
- Documentation requirements of the operator. (6)
The introduction of dental operating microscopes in our profession is definitely representative of a phenomenal qualitative leap in dental technology .
References
- A Consumer's Guide to Dentistry (Second Edition) 2002, CHAPTER 18 – Restorative or Operative Dentistry: Fillings for Teeth
- https://success.ada.org/en/career/disability-support-for-disabled-dentists#
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0161642087335535
- Carlos Murgel, DDS, PhD. MICRO: The International Journal of MicroDentistry Fall 2010 Volume 2 , Issue 1Microdentistry: Concepts, Methods, And Clinical Incorporation
- https://www.endoexperience.com/documents/Magnificationinendodontics.pdf
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/291906832_A_study_on_the_ergonomical_working_modalities_using_the_dental_operating_microscope_DOM_Part_II_Ergonomic_design_elements_of_the_operating_microscopes



















Comments