– Dr Mriganka Sekhar Ghose
Abstract
Background: This is a clinical research which specifically focusses on COVID-19 signs & symptoms in the oral & maxillofacial region, which every dentist practicing in this current time must be aware of. Symptoms such as high fever, dry cough and difficulty in breathing are the cardinal symptoms of the New Coronavirus (COVID-19) Disease but it must be acknowledged that COVID-19 does show other signs & symptoms in the oral & maxillofacial region too.
Objectives: Various other signs & symptoms of COVID-19 may be present in the oral & maxillofacial region of patients who show the cardinal symptoms of the disease, which need active research.
Methods: This clinical research is done in a dental clinic with normal inflow of patients who came for dental treatments but were having COVID-19 signs & symptoms. General methods of examination such as inspection, palpation, percussion & auscultation were performed.
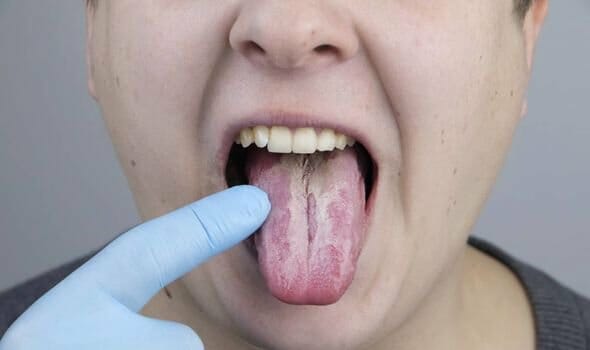
Outcome: Some patients who were having the COVID-19 symptoms of dry cough, high fever & difficulty in breathing also exhibited other signs & symptoms in the oral & maxillofacial region which rarely are taken into account by the clinicians involved. These signs & symptoms includes gingivitis, xerostomia, oral ulcerations, loss of taste sensations and bad breath, and must be taken seriously.
Keywords: Gingivitis, Loss of taste sensation, COVID-19, bad breath, ulcerations in the oral mucosa ,salivary glands.
Novelty
This research indicates that COVID-19 signs & symptoms , which are specific to the oral & maxillofacial region,may be present and may be treated by the dental surgeon in a symptom based approach.
Study Objective
To find out whether COVID-19 shows signs & symptoms specific to the oral & maxillofacial region.
Methodology
This research was put into paper after taking medical literature into consideration and instances in the clinic where patients came with COVID symptoms & on examining the oral cavity, it was found that all these patients were showing various other signs & symptoms. All patients showing classical COVID symptoms were carefully evaluated for other oral signs and symptoms. This was done under strict disinfection and sterilization protocol as recommended by authoritative bodies. The symptoms were noted and symptomatic relief was given. It must be noted that none of these patients were having carious teeth or third molar impaction problems.
- For patients who showed gingival bleeding, a prescription of 2 tablets of Vitamin C daily along with an anti plaque tooth paste (X tar), a Chlorhexidine mouthwash (Clohex ADS), a Metronidazole ointment (Metrohex) to be applied on the gingiva, and oral Doxycycline 100mg was given.
- For patients with xerostomia, complete abstinence from smoking was advised and a prescription of a nutritional supplement (Becadexamin) and a medicine to stimulate salivation (Wet Mouth) was given. Nicotine replacement therapy was not advised as patient was showing symptoms of COVID-19.
- For patients with oral mucosal ulcerations, a prescription of topical paste such as triamcenolone buccal paste (Caziq), nutritional supplement (A to Z Multivitamin) and oral Rebemipide was given.
- For the patients with gingivitis, the patients were prescribed only medicines & no oral prophylaxis procedure or scaling could be performed, as it was a COVID pandemic period & all precautionary measures were taken to prevent the spread of coronavirus through aerosols or droplets.
Discussion
Pathophysiology Of The Oral & Maxillofacial Signs & Symptoms Of Covid-19
- Gingivitis:Inflammation and bleeding in the oral tissue, known as gingivitis, is believed to be caused by an overall increase in inflammation due to elevated levels of cytokines and interleukins that are initiated by the SARS COV-2 virus. COVID-19 disease severity has been linked to immune disregulation leading to a cytokine storm. Periodontal disease can exacerbate this condition by increasing circulating cytokine levels, particularly interleukin-6 (IL-6), which is implicated as a major factor in cytokine storms.
- Xerostomia (Dry Mouth):COVID-19 may cause dry mouth, or xerostomia, due to several factors. Mouth breathing can dry out oral tissues, especially without proper hydration.
- Oral Ulcerations & Gingival Tissue Breakdown:Oral ulcerations and breakdown of gingival tissue have been associated with COVID-19 due to vascularity anomalies resulting from viral damage to blood vessels. William Li, MD, President and Medical Director of the Angiogenesis Foundation, describes the process by which the virus gains entry into the endothelial cells lining blood vessels via the ACE 2 receptor and damages them, leading to oxygen deprivation and tissue necrosis such as oral ulcerations.
- Loss Of Taste & Smell:
Loss of taste and smell may be among the earliest indications of COVID-19. The mechanism behind these symptoms is suspected to be viral disruption of cranial nerves 1, 7, 9, and 10, as well as supporting cells of neural transmission.
Many doctors continue to question the direct link between SARS-COV-2 & oral disease, but studies do suggest that the mouth might be most vulnerable area to this coronavirus due to the abundance of ACE2 (Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2) receptor in oral tissue. The ACE 2 receptor has been well documented to be the target receptor of SARS-COV-2 virus & the portal of entry into the human cell. A new preprint study found that compared with other oral tissues, cells of salivary glands, tongue & tonsils carry the most RNA linked to the proteins that the SARS-COV-2 virus needs to infect the cells, namely, the ACE 2 & an enzyme called TMPRSS.
Sample Size
Total of 6 patients were taken into account for this clinical research.
Project Implementation
There was no specific strategy for enrolling of participants in this regular check up. Participants were normal patients who came for dental treatments.
Outcome
Through this research, it was found that other than the main cardinal signs & symptoms of COVID-19,COVID-19 shows signs & symptoms in the oral & maxillofacial region too.
Limitations
The limitations of this study that only 6 people were taken into account for research. To strongly conclude that COVID-19 shows signs & symptoms in the oral & maxillofacial region, we need to include more people in the sample size.
Future Scope
More people (patients) need to be taken into account for this clinical research.
Institutional Support
Self (Dr Mriganka Sekhar Ghose’s Dental clinic, Assam).
Reference Literature
- Gheblawi M, Wang K, Viveirosa, etal. SARS-COV-2 receptor & regulator of the renin angiotensin system, celebrating the 20th anniversary of the discovery of ACE2 .CircRes.
- Janaka T, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T. Immunotherapeutic implication of IL-6 blockage for cytokine storm.Immunotherapy 2016.
- Xu J, Li Y, Gan F, Du Y, YaOY. Salivary glands potential reservoirs for COVID-19 asymptomatic infection.J.Dent Res 2020;99 (8):998.doi10.1177/00220345209185/.
- Lanese N COVID-19 infects the mouth.Could that explain patient’s taste loss.Live science, November 2,2020.
- Anarthe, Raju, Mani, Amit, and Saklecha, Sejal. ‘Oral Manifestations of COVID-19: A Review’. 1 Jan. 2023 : 39 – 49.
- Lin, Weiming et al. “The oral manifestations and related mechanisms of COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection.” Frontiers in cellular neuroscience vol. 16 1006977. 4 Jan. 2023, doi:10.3389/fncel.2022.1006977
- Yan, Wudan. “Their Teeth Fell Out. Was It Another Covid-19 Consequence?” The New York Times, 26 Nov. 2020, www.nytimes.com/2020/11/26/health/covid-teeth-falling-out.html.
- Soares, Ciro D. DDS, PhD*,†,‡; Souza, Lucas L. DDS*,§; de Carvalho, Maria G.F. MS, PhD*,†; Pontes, Hélder A.R. DDS, PhD*,§; Mosqueda-Taylor, Adalberto DDS, MSc‡; Hernandez-Guerrero, Juan C. DDS, PhD∥; do Nascimento Medeiros, Sanderson D. BBiomedSc¶; de Oliveira Sales, Alexandre MD, MSc¶; Alves, Fábio A. DDS, PhD#,**; Lopes Pinto, Clóvis A. MD, PhD††; de Almeida, Oslei P. DDS, PhD*. Oral Manifestations of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Comprehensive Clinicopathologic and Immunohistochemical Study. The American Journal of Surgical Pathology 46(4):p 528-536, April 2022. | DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000001825
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are that of the author alone and does not necessarily reflect the official policy of DentalReach. DentalReach does not endorse, promote or associate with this product and this article is meant for informative purposes only.



















Excited to be here
Thanx ????