– Dr. Madhulika Banerjee

Today, whenever and whatever starts with “E”, we think that it is something related to the internet like E-Book, E-newspaper, E-magazine, etc. But what about E-Cigars! Now see, E-Cigars does not mean you can smoke online!
E-Cigars or electronic cigars or e-cigarettes are the battery-operated devices that people use to inhale aerosol which contains nicotine (though not always), flavorings and other types of chemicals. They are also known as Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems (ENDS) and this term includes various types of devices like :
- vapes,
- e-hookahs,
- e-pipes and
- e-cigars.
These devices work by heating the liquid so that it turns into a vapour for the smoker to inhale, or ‘vape’. E-cigarettes vary widely in design as well as appearance. There has been a dramatic rise in the use of e-cigarettes among youth and young adults.The availability and popularity of flavored e-cigarettes is one of the important concern regarding the potential public health implications of the products. The youth is excited and happy to know about the availability of e-cigarettes with sweet flavors, which will facilitate nicotine addiction and simulate smoking behavior. Flavors have been used for many years to attract the youth towards tobacco products to mask the flavor and harshness of tobacco.
So, do you know what does the vapor of an E-Cigar consist of? If “NO”, then let’s see:
- Propylene glycol
- Glycerin
- Nicotine
- Heavy metals
- Flavors
- Traces of toxicants
- Carcinogens
- Metal nanoparticles
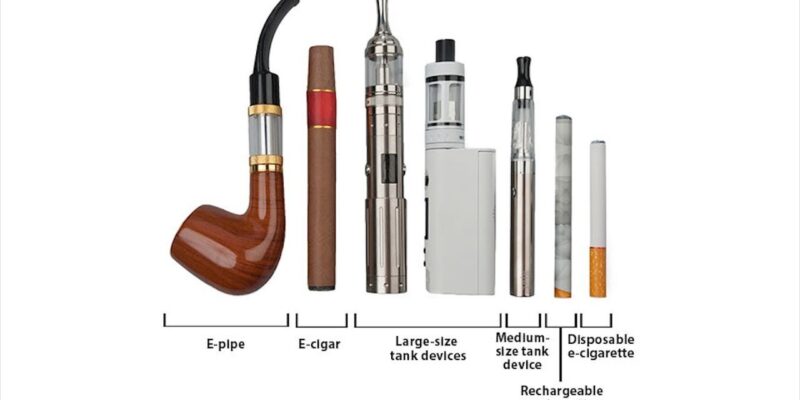
E-CIGARETTE DEVICES
l First-generation e-cigarettes: These were mostly similar in size and shape to conventional cigarettes, with a design that also simulated a traditional cigarette in terms of the colors used (e.g., a white body with tan mouthpiece). These devices are also known as cigalikes, but there were also other products designed to simulate a cigar or pipe.
l Second-generation devices: These include products whose shapes are like pens, are comparatively larger and cylindrical, and are sometimes known as “tank systems” in a nod to the transparent reservoir that holds larger amounts of e-liquid than previous cartridge-containing models.
l Third and fourth generation devices consists of a diverse set of products and, esthetically, constitute the greatest departure from the traditional cigarette shape, as many are square or rectangular and feature customizable and rebuildable atomizers and batteries.
Unintentional exposure to and poisoning from e-cigarette solutions containing nicotine have increased dramatically in the United States since 2011. Although symptoms of acute nicotine toxicity are generally mild and resolve within 12 hours with no treatment, large exposure can be fatal.1 One child death caused by ingestion of liquid nicotine has been reported in the United States.2
The Child Nicotine Poisoning Prevention Act of 2015, which was enacted nationally in January 2016, requires containers of liquid nicotine to be in child-resistant packaging; nonetheless, there continue to be thousands of reports of exposure to e-cigarette liquid nicotine yearly to the National Poison Data System.3 In addition, the lithium-ion batteries used in e-cigarettes have exploded, leading to burns and fires.4
Effects of E-cigars on general and oral health
If you think that smoking via e-cigarettes is safe and is not going to affect your lungs, then for sure you are in a wrong path of your imagination. Have you ever imagined why more teenagers are getting into this smoking trend? The foremost reason is not the habit of their smoking, but the swag factor which they love to flaunt in front of their so called friends. These E-Cigars are the one which will judge your status in the society. And you just cannot always blame the smokers.So, now it’s the time to point out those who feel that smoking is a fashion in today’s era.
How cigars can affect your general health
- Lung Cancer
- Stomach Cancer
- Bladder Cancer
- Heart Disease
- Respiratory diseases which causes difficulty in breathing.
Electronic cigars and oral health
Smoking is one of the most important risk factors for oral cancer, periodontal diseases as well as implant failures. It has been claimed by the E-cigarette companies that e-cigars can improve oral health by providing alternatives to smoking, but this role is still unclear. The effect of e-cigarette on oral health is not completely understood and a debate is still going on among many scientists and clinicians. It has been studied that plaque index, periodontal probing, and clinical attachment loss were significantly higher in smokers compared to other groups and there was no difference in self-perceived gingival pain and swelling between e- cigarette users and no smokers.
It is argued that e-cigarette use is not as hazardous to periodontal health compared to cigarette smoking. 5 However, bleeding in probing (a classical marker for periodontal disease severity) was masked in both smokers and e-cigarette users compared to no smokers – this is likely due to the vasoconstriction effect of nicotine on gingival blood vessels.5 Since periodontal and gingival cells are firstly targeted by e-cigarette aerosols, there is a concern that e-cigarette may have an adverse effect on periodontal as well as on gingival oral health.
Explosion of e-cigarette inside the smoker’s mouth results in abdominal burns, oral lacerations, teeth fractures, etc. Explosion can occur due to various factors like e-cigarette device design, battery quality, and compatibility between the device and the charger.
While taking medical and dental history, dental surgeons should identify all forms of tobacco and nicotine use (cigars, cigarettes, e-cigarettes, chewing tobacco, and other forms). Dentists should advise patients about the unknown and deadly danger of e-cigarette use.
Role of dentists in E-cigarette cessation counselling
Due to the oral health implications of tobacco use, dental practices provide a uniquely effective setting for tobacco use recognition, prevention, and cessation. Dental professionals can help smokers quit by continuously identifying patients who smoke, advising them to quit, and offering them details and facts about the process of cessation treatment. The dental team can play a major role in the making of tobacco-free societies and individuals through participation in community and in counselling their patients to quit smoking. Therefore, dental visits serve an opportunity to identify and support patients quit smoking.
Lack of training and inadequate knowledge of tobacco cessation counselling (TCC) are known barriers to counselling practices among dental practitioners. Thus, dentists have an opportunity to play a role in promoting healthy lifestyles by incorporating tobacco cessation programs into their practice, only if the dental students are trained well.[1]
Conclusion
Tobacco use is one of the most important cause of several diseases, disabilities and death. Hence, every measure should be taken to eliminate its consumption completely.
First try to avoid smoking, then try to eliminate it from your life and after you have completed your trial process, then finally just give a big “STOP” to it. You can become an example for the young teenagers, let’s see how:
- Don’t allow anyone to use E-cigarettes or other tobacco products around young people.
- Make sure school is tobacco-free.
- Set an example for others.
- Try visiting tobacco-free locations.
Dental teams are in perfect job to provide help for smokers who want to quit smoking and promote smoking cessation. Thus, tobacco cessation counselling (TCC) is a must for every dental practitioner. As smoking has such an adverse footprint on oral health, it’s a key priority to ensure that all the members of the dental team engage with tobacco users and help them out to quit smoking forever.
References
1. Mayer B. How much nicotine kills a human? Tracing back the generally accepted lethal dose to dubious selfexperiments in the nineteenth century. Arch Toxicol. 2014;88(1):5–7.
2. Eggleston W, Nacca N, Stork CM, Marraffa JM. Pediatric death after unintentional exposure to liquid nicotine for an electronic cigarette. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016;54(9): 890–891.
3. Govindarajan P, Spiller HA, Casavant MJ, Chounthirath T, Smith GA. E-cigarette and liquid nicotine exposures among young children. Pediatrics. 2018;141(5):e20173361.
4. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Public Health Consequences of E-Cigarettes. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; 2018
5.Javed F, Kellesarian SV, Sundar IK, Romanos GE, Rahman I. Recent updates on electronic cigarette aerosol and inhaled nicotine effects on periodontal and pulmonary tissues. Oral Dis. 2017 Nov;23(8):1052-1057.


















Thanks for the blog.Nice dental information.