Keywords 3D Printing , Prosthodontics
Introduction
Prosthodontics is a specialized field of dentistry that focuses on the restoration and replacement of damaged or missing teeth and their supporting structures. Traditionally, prosthodontic treatments involved a labor-intensive process, including impressions, model fabrication, and manual crafting of prosthetic devices. However, the advent of 3D printing technology has revolutionized the field, offering numerous advantages in terms of precision, customization, and efficiency. This essay explores the profound impact of 3D printing in prosthodontics, discussing its applications, benefits, and future potential.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Prosthodontics
- Precision and Customization:3D printing technology enables a level of precision and customization that was previously unattainable. Every dental restoration can be tailored to fit the patient’s unique anatomy, ensuring better outcomes and patient satisfaction.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: By eliminating many manual steps in the traditional prosthodontic workflow, 3D printing significantly reduces production time and labor costs. Dentists can streamline their processes, seeing more patients and offering competitive pricing.
- Improved Patient Experience: Custom-made prosthetics often result in improved patient comfort and aesthetics. This not only enhances the patient experience but also contributes to better long-term oral health outcomes.
- Reduced Material Waste: Traditional prosthodontic methods can generate significant material waste, particularly in casting and modeling processes. 3D printing produces minimal waste as it adds material layer by layer, reducing environmental impact.
Applications of 3D Printing in Prosthodontics
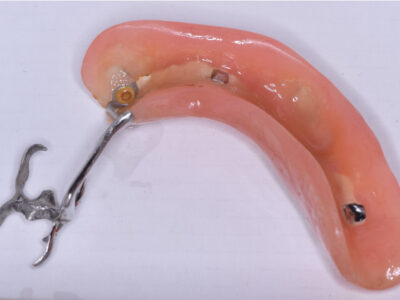
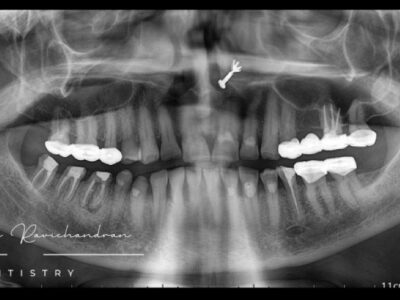
- Custom Implantology: One of the most significant applications of 3D printing in prosthodontics is in the creation of custom dental implants. By utilizing patient-specific scans and digital design software, prosthodontists can craft implants that perfectly fit the individual patient’s oral anatomy. This level of precision minimizes the risk of implant failure, improves comfort, and reduces recovery time.
- Removable Partial Dentures: 3D printing technology allows for the production of removable partial dentures with exceptional accuracy. Dentists can obtain digital impressions of the patient’s mouth and create a highly personalized prosthesis. This not only enhances patient comfort but also ensures a better fit and aesthetics.
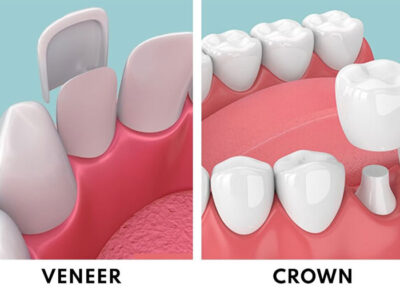
- Crown and Bridge Restorations: Traditional crown and bridge restorations involve a multi-step process, including impressions, wax-ups, and casting. 3D printing streamlines this process by directly printing crowns and bridges from digital designs. This eliminates the need for many manual steps, reducing the chances of errors and saving time for both dental professionals and patients.
Challenges and Future Potential
While 3D printing has brought tremendous advancements to prosthodontics, there are still challenges to overcome. Some of these include:
- Material Selection: Developing biocompatible, durable, and esthetically pleasing materials suitable for 3D printing in prosthodontics is an ongoing challenge.
- Regulation and Training: Ensuring that dental professionals are adequately trained in 3D printing techniques and navigating the evolving regulatory landscape for dental 3D printing are crucial considerations.
- Cost: The initial investment in 3D printing technology can be substantial, potentially limiting access for smaller dental practices. Despite these challenges, the future of 3D printing in prosthodontics looks promising. Ongoing research and development efforts are likely to yield improved materials, more user-friendly software, and increased affordability. As a result, the technology will become more accessible and widely adopted, further enhancing patient care in the field of prosthodontics.
Conclusion
3D printing has transformed prosthodontics by offering precision, customization, efficiency, and improved patient experiences. The applications of 3D printing in prosthodontics are extensive, from custom implants to crowns and bridges. While challenges exist, ongoing advancements in materials and training are paving the way for a brighter future in which 3D printing will continue to revolutionize dental restorations, ultimately benefiting both dental professionals and their patients.
















Comments